- Home
- What Is Colitis
What Is Colitis Disease
Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
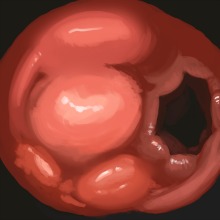
What is colitis? Inflammation of the colon (large intestine). Types are microscopic colitis, chemical colitis, infectious colitis, ulcerative colitis (UC), ischemic colitis, pseudomembranous colitis, drug-induced colitis, radiation colitis, lymphocytic colitis, collagenous colitis.
Related Disorders Crohn's disease, irritable bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diverticulitis
Also Referred To As ulcerative proctitis, left-sided colitis, distal colitis, pancolitis, universal colitis, fulminant colitis
Anyone that has been diagnosed with colitis will tell you it's no small condition to overcome. It can be debilitating in the sense that you never know when a flare up might occur. So, one minute you can be in a meeting at work and the next you feel as if you need to run to the bathroom or else diarrhea will happen right there.
Your doctor will normally prescribe a cocktail of medications to be taken on a daily basis and other drugs for complications as needed. Among the drugs prescribed could include: Lialda, Endocort, Librax, Pamelor, Rowasa, Canasa, Asacol, Prednisone, and others.
What is Colitis Characteristics? arthritis, chronic diarrhea, bloody stools, mucus in stools, anemia, hair loss, malnutrition, abdominal pain, kidney stones, fatigue, weight loss, appetite loss, low sex drive, fever, shock, night sweats, failure to grow in children
What is Colitis Food Intolerance? fructose, wheat/gluten, dairy/milk
Fructose intolerance is an inherited inability to digest the sugar because the digestive system is missing an enzyme. These people can't turn fructose into glucose in order for it to be absorbed by energy. If a person ingests a large quantity of fructose, major side effects may occur such as bowel irritation accompanied by intestinal gas, cramping, and diarrhea.
Stages of Ulcerative Colitis During the early stages of colitis, warning signs may present themselves such as extreme gas. The inflammation always starts in the rectum. The severity of the condition depends on the amount of inflammation on the colon. This early stage may also be confused with Crohns disease.
In mild cases, such as with ulcerative proctitis where only the rectum is affected, the only sign could be bloody diarrhea. As inflammation effects more of the rectum and colon; pain, tenesmus (urgency to defecate), and cramping occur. Having diarrhea more than 10 times a day is not uncommon. The most severe case of colitis is pancolitis/universal colitis. Fulminant colitis is a form of pancolitis and is even more severe. If you have fulminant colitis, it's more difficult to treat than other forms of colitis. There is also a risk of developing megacolon (dilation of the colon) and peritonitis (colon rupture) which can lead to death.
Colitis Surgery
What Is Colitis Surgery? If you have ulcerative colitis, doctors consider surgery a cure for the illness. It is not an easy decision to make because it requires deciding whether to try and endure the daily frustration of UC symptoms or to live with the symptom free but complicated conditions life after surgery offers.
A good majority of people who've had surgery comment that it is a relief to not have to suffer horribly with the illness and be UC free. Still, there are some who will fight tooth and nail to avoid surgery and would rather try a combination of supplements and going on a colitis diet. What is colitis diet? The diet contains specific foods and supplements that are needed to heal the colon. Sensitivity/allergic foods are strictly avoided. See the link above for more information.
The three types of surgeries available are partial colectomy, total proctocolectomy with permanent ileostomy, and proctocolectomy with ileoanal pouch.
What Is Colitis Types?
What is colitis ulceration? small open sores or ulcers. Characterized by chronic bloody diarrhea and profuse gas. Other symptoms include weight loss, malnutrition, hair loss, abdominal cramping, large amounts of mucus in stool.
Microscopic colitis: Two types of microscopic colitis and they are lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis. Lining of the colon appears normal to the eye. Inflammation of the colon is only visible by colonoscopy and biopsy.
Chemical colitis: Acute inflammatory colitis with mucosal damage due to self-administration of enemas. The harmful 'cleansing' agent could be vinegar, soap, hydrogen peroxide, etc. also known as soap colitis. Symptoms include pain and diarrhea. Sever conditions can lead to intestinal gangrene or sepsis.
Infectious colitis: This type of colitis can be caused by different infectious agents including bacterial, viral, parasitic, or fungal. Diagnosed by stool sampling, blood culture, and endoscopic biopsy. Symptoms include watery bloody diarrhea, cramping, nausea, fever, dysentery.
Ischemic colitis: Lack of blood supply and decreased blood flow to the colon which causes irritation. Symptoms include small amounts of bloody diarrhea, fever, and cramp-like left-sided abdominal pain.
Pseudomembranous colitis: An acute disorder affecting the colonic and rectal mucosa with overgrowth of Clostridium difficile bacteria. Characterized by yellowish pseudomembranes along the colon and associated with the administration of antibiotics. Usually occurs in the hospital due to antibiotic therapy. Candida albicans (yeast infection) has also been associated with causing diarrhea.
Drug-induced colitis: Drugs that cause inflammation to the normal bowel or pre-existing inflammatory bowel disease.
Radiation colitis: Caused by radiation-induced changes to the colon. Usually found in patients that have undergone preoperative short and long course radiotherapy for abdominal/pelvic tumors and rectal cancer.
Lymphocytic colitis: A type of microscopic colitis that involves white blood cells called lymphocytes that work to fight off infection but can also cause inflammation. Symptoms include watery non-bloody diarrhea with abdominal cramping and urgency that usually go away after bowel movement.
Collagenous colitis: A type of microscopic colitis that causes inflammation of the colon with a thickened collagen layer in the lining of the colon. Symptoms include watery non-bloody diarrhea with abdominal cramping and urgency that usually go away after bowel movement.
Related Pages

Popular Articles


